Non-line-of-sight surface reconstruction using the directional light-cone transform
Sean I. Young, David B. Lindell, Bernd Girod, David Taubman, Gordon Wetzstein
We propose a joint albedo–normal approach to non-line-of-sight (NLOS) surface reconstruction using the directional light-cone transform (D-LCT).
Video
Abstract
We propose a joint albedo–normal approach to non-line-of-sight (NLOS) surface reconstruction using the directional light-cone transform (D-LCT). While current NLOS imaging methods reconstruct either the albedo or surface normals of the hidden scene, the two quantities provide complementary information of the scene, so an efficient method to estimate both simultaneously is desirable. We formulate the recovery of the two quantities as a vector deconvolution problem, and solve it using the Cholesky–Wiener decomposition. We show that surfaces fitted non-parametrically using our recovered normals are more accurate than those produced with NLOS surface reconstruction methods recently proposed, and are 1,000× faster to compute than using inverse rendering.
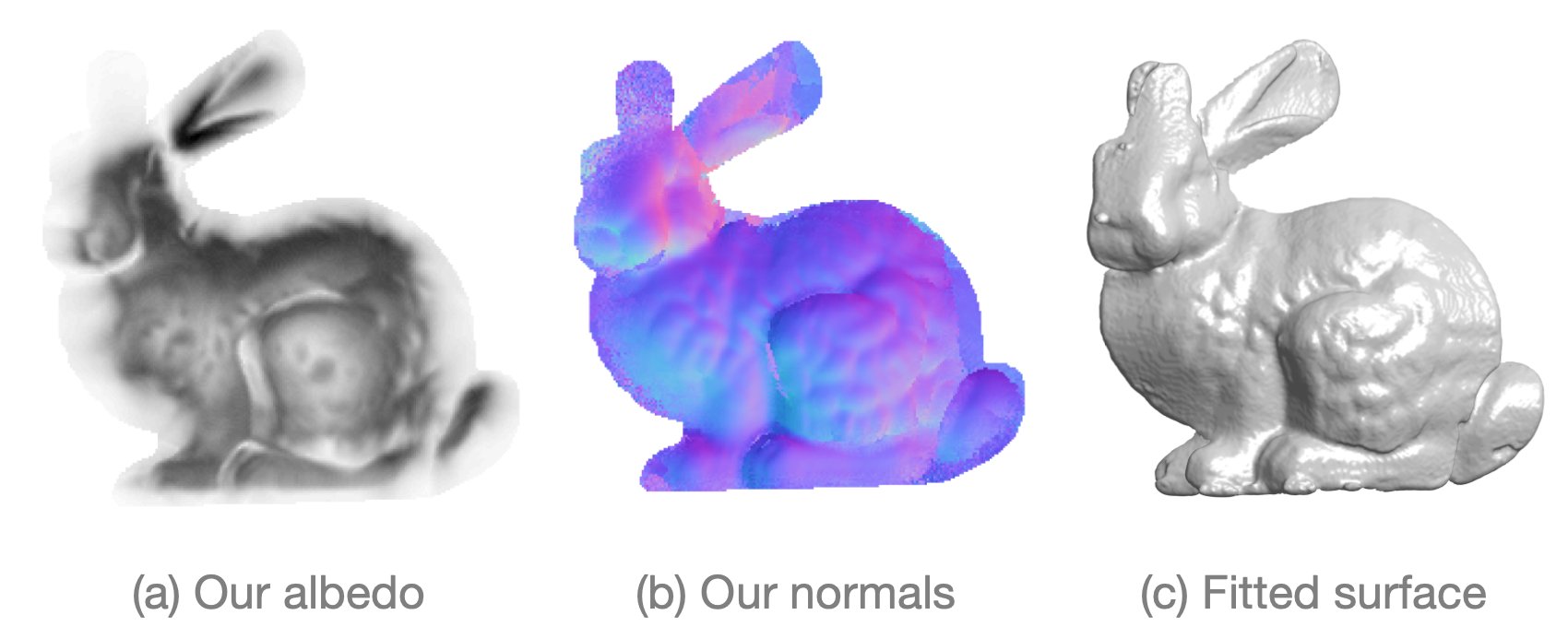
NLOS surface reconstruction via the D-LCT: Existing NLOS imaging methods typically recover only the albedo of the hidden scene. Ae Directional LCT recovers both the albedo (a) and the surface normals (b) of the scene, allowing us to reconstruct the hidden object surface with finer detail (c).
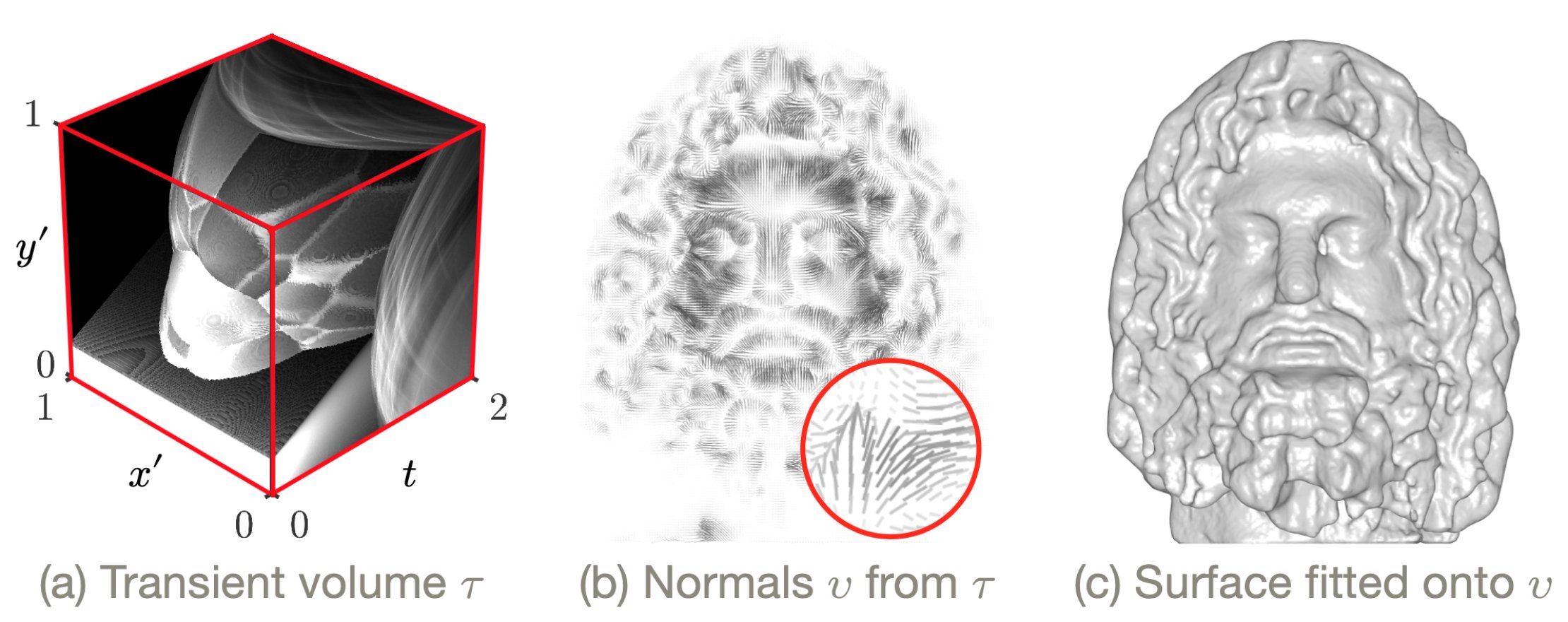
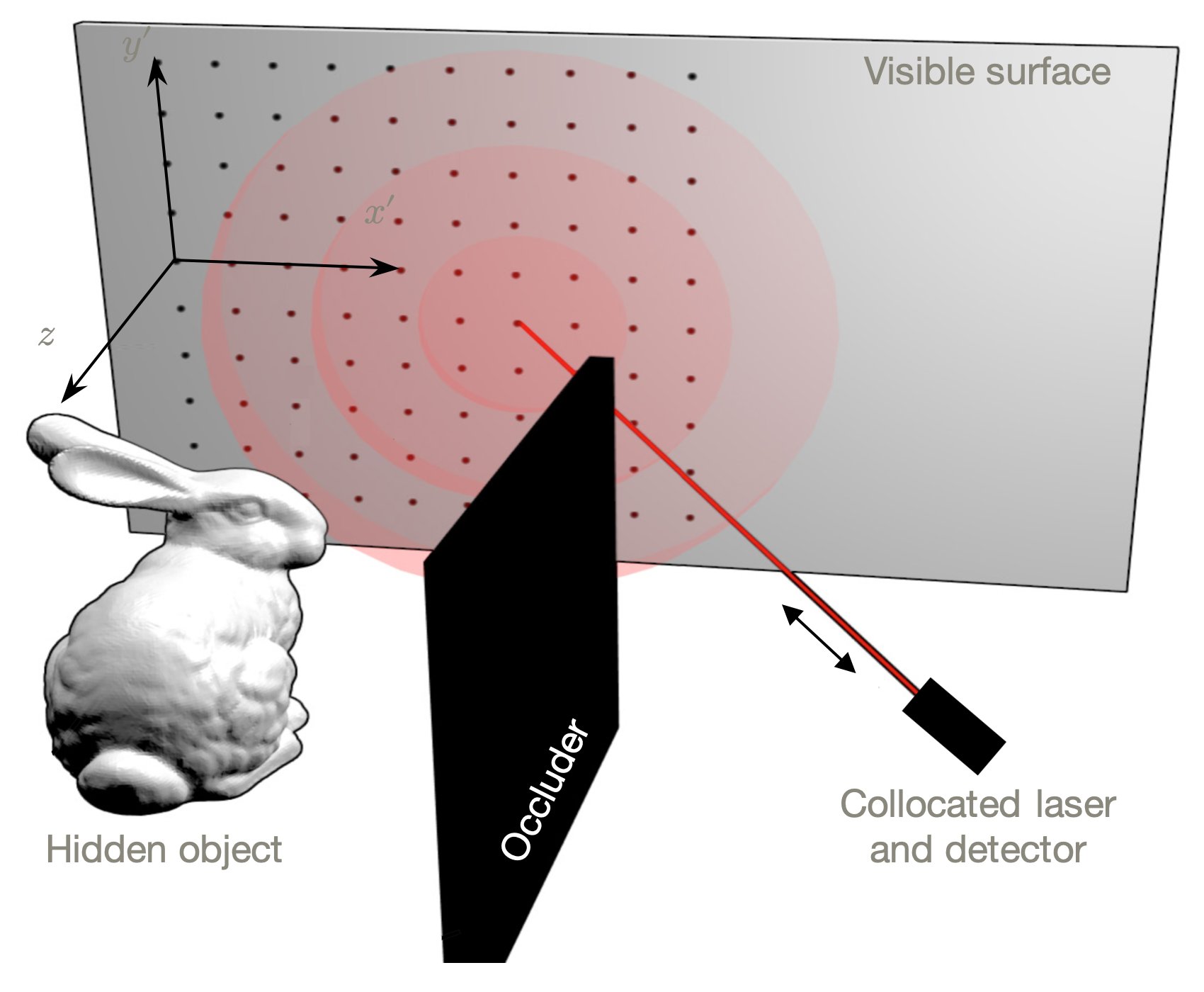
Method overview: A 1m × 1m × 2ns volume 𝜏 of transients (a) is filtered using the directional light-cone transform to obtain the surface normals (b). We integrate the surface normals to obtain the final reconstructed surface (c).



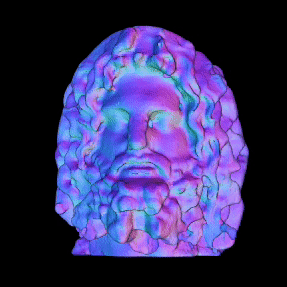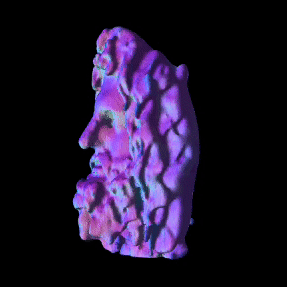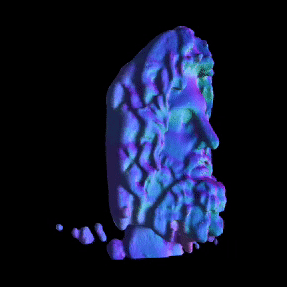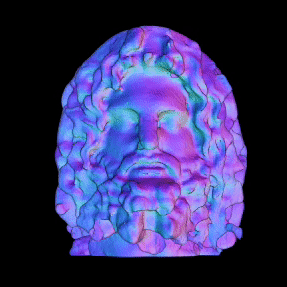

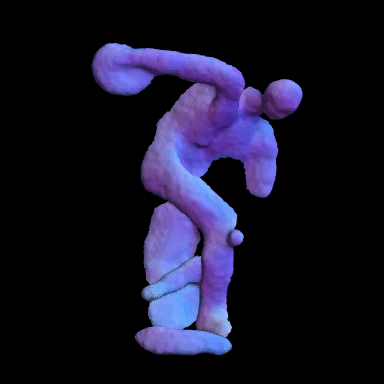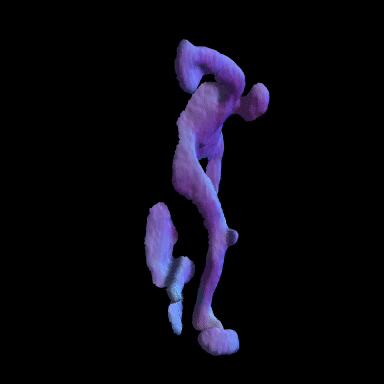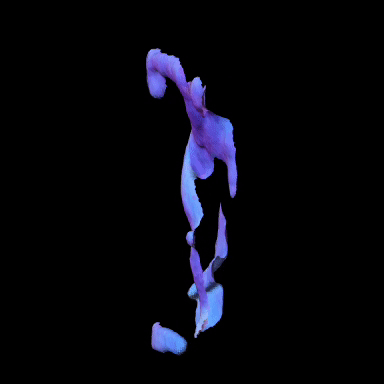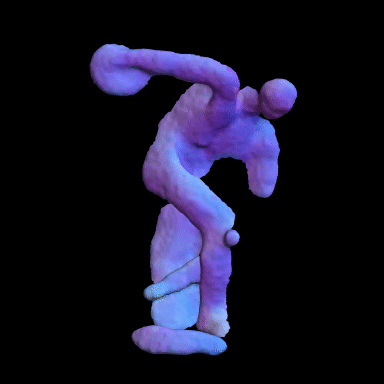
Simulated Results showing ground truth object (left) and reconstructed NLOS surface with color-coded normals (right).

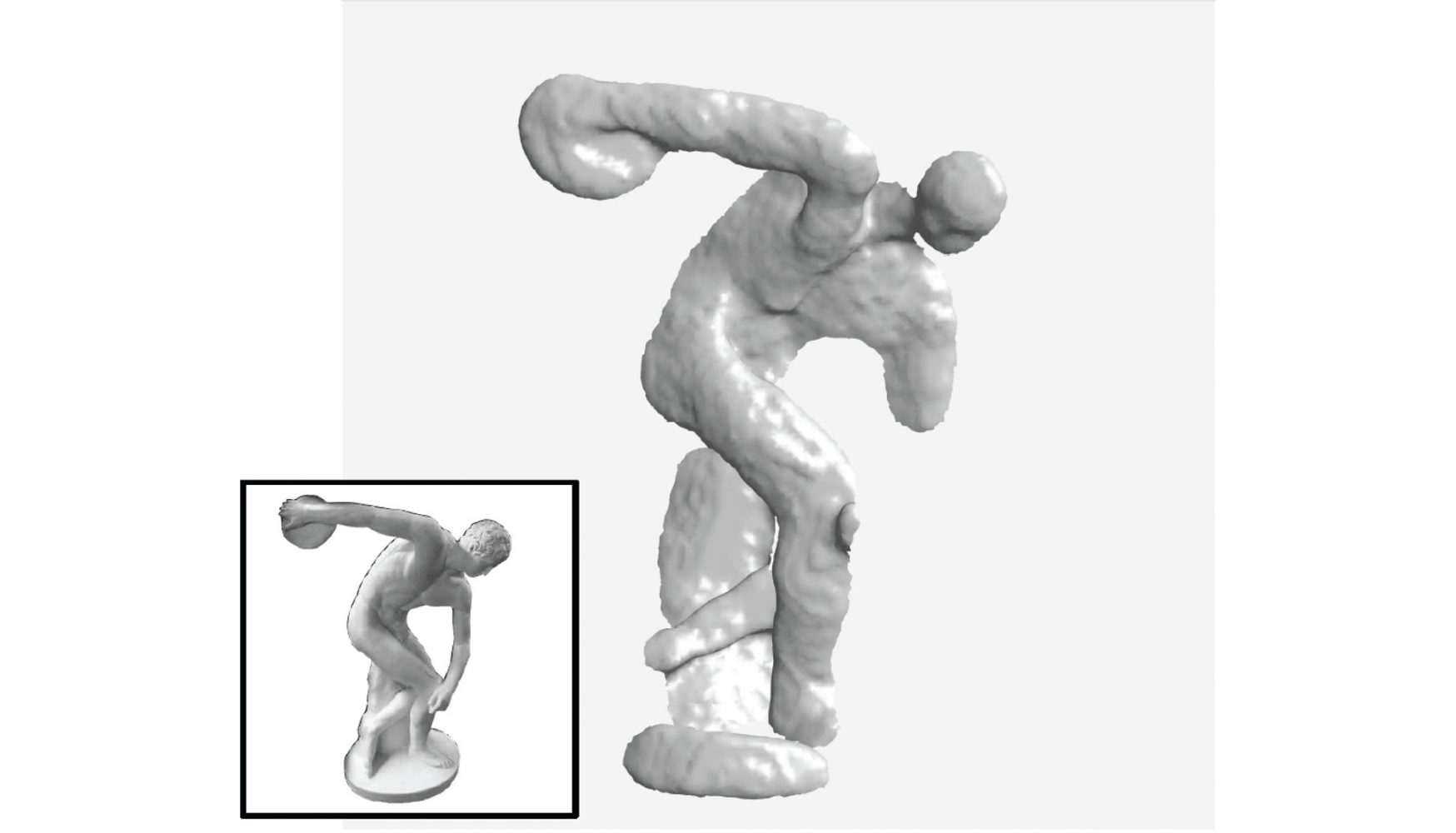
Comparison of Related Methods. Recent NLOS surface reconstruction methods, including Fermat Flow [Xin et al., 2019] and Beyond volumetric Albedo [Tsai et al. 2019], fail to reconstruct the complex geometry of this object from measured data. The Directional Light-Cone Transform recovers high-quality geometry and surface normals (right).
Acknowledgments
We thank M. J. Galindo for help with the ZNLOS dataset and I. Gkioulekas for help with the baseline comparisons. D.L. was supported by a Stanford Graduate Fellowship. G.W. was supported by an NSF CAREER Award (IIS 1553333), a Sloan Fellowship, by the KAUST Office of Sponsored Research through the Visual Computing Center CCF grant, the DARPA REVEAL program, and a PECASE by the ARL.
Citation
@inproceedings{Young:2020:dlct,
author = {Sean I. Young and David B. Lindell and Bernd Girod and David Taubman and Gordon Wetzstein},
title = {Non-line-of-sight Surface Reconstruction Using the Directional Light-cone Transform},
booktitle = {Proc. CVPR},
year = {2020},
}